
You have the equipment ready, the lighting in position and the hydroponic system or planting pots are in place. It’s time to start the actual growing of the cannabis plant. It’s time to give your garden life. Cannabis growing takes place in four main stages: Cannabis germination, Cannabis seedling, Vegetative stage, and Flowering. We will cover the Germination and Seedling stage extensively in this guide, but first, let’s start with some general information about the cannabis plant itself.
About cannabis plant
The history of the Cannabis plant dates back thousands of years. According to various research accounts, the plant has been used as food, medicine, and for ritual purposes for many years. The first record of Cannabis cultivation, apparently for medicinal reasons, appeared in 28th century B.C.E. But other sources also reveal that traces of THC, which is the key psychoactive component in Cannabis, were found in an almost 3000-year old Egyptian mummy.
Most people today refer to the Cannabis plant as Marijuana, which is a universal term for the female Cannabis plant that generates flower buds. Another term, hemp, refers to Cannabis that is grown for various industrial applications.
Types of cannabis plant
Although cannabis is available in three main types (Cannabis Sativa, Cannabis Indica, and Cannabis Ruderallis), the strains we know and love are all hybridized children. Every strain has one or another type of dominance. Therefore, before buying the seeds, you should read more about them and decide which type you would like more.
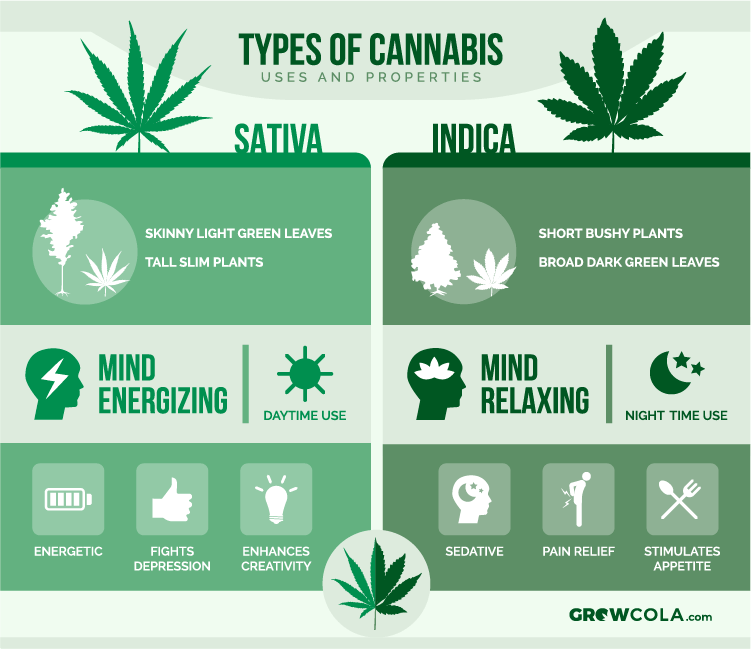
Cannabis Sativa
Cannabis Sativa is physically the most fashionable and probably the world’s most popular type. Most news media, textbooks, and drug-prevention journals use pictures of the plant. The Sativa species originate from the middle and equatorial countries. It is widespread in countries such as Brazil, Indonesia, Thailand, South Asia, India, and others. All the same, the Sativa is also prevalent in other parts of the world.
One of the things to note about the Sativa plant is that it likes warmer and humid tropical climates. These areas experience stable temperatures throughout the year. In equatorial countries, daylight hours are constant – both day and night last 12 hours regardless of darkness. The Sativa plant adapts to time and grows during the flowering period as well, making the flowering period longer.
It’s also important to point out that Sativa blooms longer than other species and produces higher yields with higher levels of THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). This type of Cannabis grows taller, thinner, and more spacious plants. Compared to other varieties, they have more space between the resins. They also have bigger roots and fewer, thinner, and longer leaves. Besides, they have a longer flowering period.
Finally, Sativa delivers a sweeter, fruity, and sharper aroma. Exposure to this plant provides more euphoria, ascension, more mental activity, increased creativity, and even physical movement. That really helps with depression!
Top strains of Cannabis Sativa are Sour Diesel, Purple Haze, and White Widow.
Cannabis Indica
Both Cannabis Sativa and Cannabis Indica are the two main species of the marijuana plant grown for medical interest. This type of marijuana plant grows lower but firm and thinner. They are leafier and bushier than the Sativa plant. Cannabis Indica is wider and denser than the Sativa plant and produces shorter and heavier buds with shorter thicker leaves. This helps the plant to absorb as much sunlight as possible.
This type of marijuana plant originates from the subtropical climate belt between 30 and 50 degrees north and south of the equator. Cannabis Indica is common in Pakistan and Afghanistan. These plants are more sensitive to the number of night and day hours. After 12 hours of the day and 12 hours of the night, they start blooming and the first flowers show up within a couple of weeks.
Since the Indica plants are smaller with shorter growth and flowering times, they can have four or even six harvests per year. This makes them a preferable choice for domestic growers. The Indica plant delivers higher levels of CBD (Cannabidiol), which makes it more popular for therapeutic purposes, acting more on the eyes, suppressing, relaxing, relieving pain, appetite, and helping to fall asleep so it’s more suitable for evening use.
Cannabis Indica has a strong, mildly acidic aroma, reminiscent of citrus fruits. Top strains: Pineapple Kush, Granddaddy Purple, and Northern Lights.
Cannabis Ruderalis
The Cannabis Ruderalis is a little-known subspecies of the marijuana plant. It is the smallest of the three types with small broad leaves, thin stems, little root and delivers fewer buds. The breed was discovered in 1924 by a Russian botanist, which is relatively recently, compared to the Sativa and Indica subspecies.
This subspecies is associated with colder and wilder regions, mostly about 50 degrees north of the Equator. It’s widespread in Russia and China where it enjoys cooler climates with shorter summers and longer winters. Ruderalis is an automatic flowering variety, so it doesn’t depend on the influence of light or darkness. Ruderalis plant begins to bloom and yields based on its maturity. This whole growth process takes two or three months from planting to harvesting.
Cannabis Ruderalis often delivers quite low levels of THC and high levels of CBD. These subspecies are mostly used for medicine and breeding new hybrids for automatic flowering.
Main stages of cannabis growth
How long a cannabis plant takes to grow mainly depends on the vegetative cycle. If you’re growing indoors, you can force it to flower even after a week when it is small, or after many weeks after forming the tree as you want. But you can’t do much if you grow outdoors, when you’re whim of the seasons and will have to wait until fall to harvest. In any case, we already mentioned that the life cycle of cannabis can be broken down into four primary stages, from seed to harvest.
Cannabis Germination (5-10 days)
The life for a cannabis plant begins with the seed. At this point, your cannabis plant is waiting for water to bring it to life. The whole process takes up to 10 days until you will see the first small root. Plant it into the soil and two rounded cotyledon leaves will grow out from the stem. These initial leaves are responsible for taking in sunlight needed for the plant to become healthy and stable.
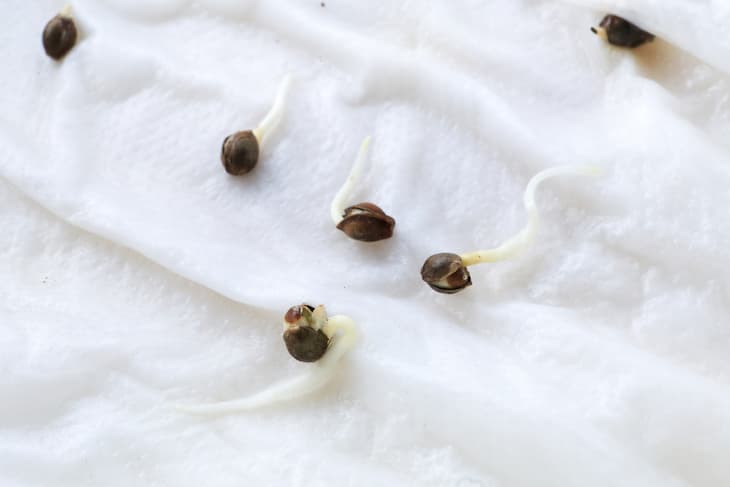

Cannabis Seedling (2-4 weeks)
Close to the end of the germination process, more roots will develop. You will begin to see the first iconic fan leaves grow, at which point your plant can be considered a seedling. In this cannabis seedling stage, you’ll notice developing more of the traditional marijuana leaves. At first, the seed will initially produce leaves with only one ridged blade. Once new growth emerges, the leaves will develop more blades (1, 3, 5, 7…). A mature cannabis plant has between 5-7 blades per leaf, although some plants may have more. At the end of our cannabis grow guide, you will find the practical process of cannabis germination and seedling stages.
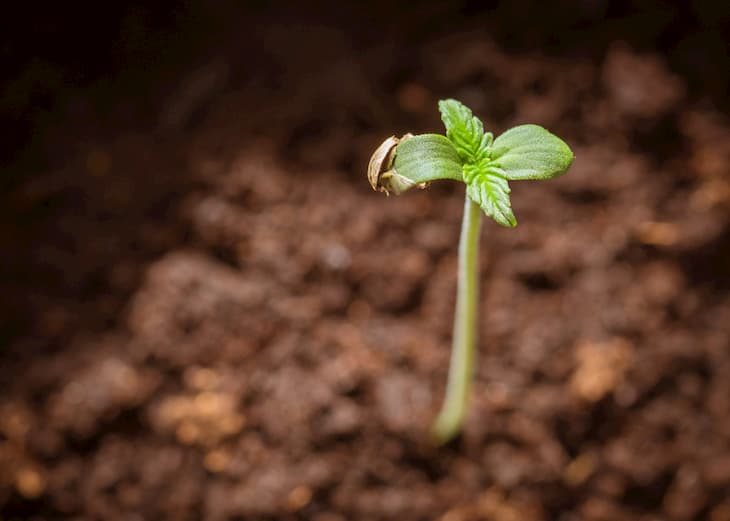

A healthy seedling should be a bright green color. At this cannabis seedling stage, the plant is very vulnerable to disease. Keep its environment clean and monitor excess moisture not to get mold.
Cannabis Vegetation (3-15 weeks)
When the plant develops 2-3 pairs of leaves, growth truly takes off. It’s the cannabis vegetative stage. If you’ve been using Fluorescent (CFL) lights until now, you need to change them to High-Pressure Sodium Vapor (HPS) or Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). More about lights you can find in our previous cannabis guide about the equipment.
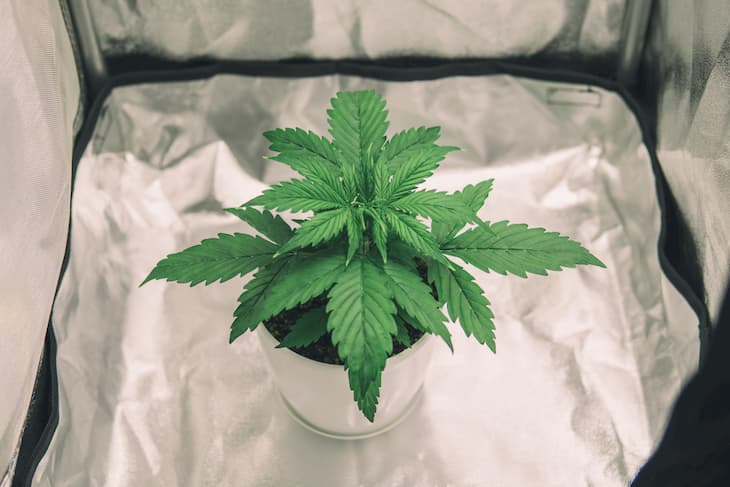

In the cannabis vegetation stage, marijuana plant needs to be transplanted into a larger pot. Foliage is developing rapidly. If your plant is not auto-flowering, it depends on you how long you will keep it in this stage. The more you keep, the bigger, the wider they can grow. After a week or two in the vegetative stage, you can start forming your tree by topping and pruning. It’s not a very easy process, but after a few harvests, you will begin to understand it better. In our next guide about the vegetative stage, we will talk about more it.
Cannabis Flowering (8-11 weeks)
The vegetative period allows the plants to develop roots and grow themselves until you put them on 12 hours of the light and 12 hours of the night. From that point, the cannabis flowering stage starts, and in a week or two, they begin to develop buds.

Of course, as mentioned earlier in this guide, some cannabis is automatic. They begin flowering depending on their maturity instead of the number of hours of light they get per day. We will cover the flowering stage in our other guide.
Seeds or clones?
You can grow Cannabis in two ways. You either buy the seeds and start from scratch or buy clones from growers who are selling them. Clones are small, few-week-old plants taken from the mature tree in the vegetative stage. Most indoor growers prefer using clones instead of seeds.
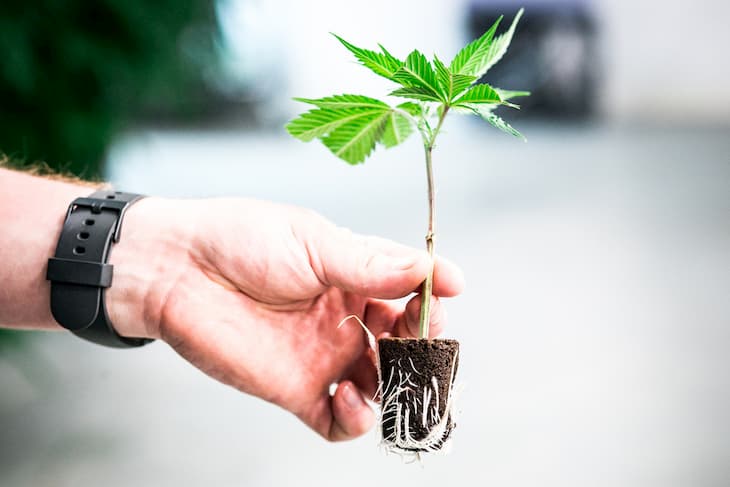

When growing cannabis, it’s always the rule of thumb to have female plants. Having at least one male plant between females will ruin your yield. Unwanted male plants are usually killed immediately to avoid pollinating the female plants, which can end up producing seeds in the buds. It’s also important to ensure that your clones are from a female plant.
Cannabis clones harvested from female plants remain female, and that’s a good way to start growing. Using clones also save you time and resources (because you skip the whole germination stage), given that someone else already did the hard part. From cutting the clones or growing from seed, caring for them for at least 10 days or more, putting them into the small root cubes, and allowing them to develop roots. That is a crucial part of the growing process, which probably not all of you might have time to do.
Ed Rosenthal writes in his book Marijuana Grower’s Handbook:
“Feminized seeds have been bred to produce only female plants. They are the solution to the problem of sexing males since all the plants are females. Germinating seeds is a more delicate operation than transplanting clones. Seeds take longer to grow and be ready to flower because rooted clones are already biologically mature and have a headstart on root development. Plants from seeds don’t reproduce exactly their parents’ traits. Seeds from a variety you saw and tasted will not grow to be exactly the same as their mother, though it will be a close approximation. Because you will discard roughly half of the plants once they can be sexed, growing from seeds can more easily put you over any legal plant count limits, or leave you with fewer plants than allowed or anticipated.”
Getting your clones
Clones are available at clone dispensaries at varying prices. Be familiar with the laws in your area before you buy it. Conduct a little research and you can find clone dispensaries that run special offers. You can get great deals on particular clones. It’s equally important to visit the dispensary to ensure that the strain you bought is actually what they say it is. Besides, it’s quite important to inspect the root system of your clones to ensure they are free of any infection or parasites.
Overall, there are pros and cons of growing from both, clones and seeds.
There are two main benefits of growing Cannabis from clones:
- Clones are cut from female plants, so they remain females. You eliminate male plants or hermaphrodites that might lead to unnecessary sexing.
- Clones save you time and help you skip the germination “hump” and most of the seedling stage that is associated with seeds. Seeds take weeks to catch up to a rooted plant. Clones are already a couple of weeks old with a developed root system and ready for vegetation stage.
Downsides of Clones
- It might be difficult to find sellers in your area. Clones are grown commercially in selected states with medical marijuana laws.
- Sometimes you might not find clones of your preferred strain, even in areas where they are legal.
- It’s easier for clones to carry diseases and pests than seeds. One infected plant can infect the entire garden. Always buy clones from authorized and professional growers.
- In most cases, you can expect a lower yield than from seeds.
For outdoor growers, clones aren’t a better option, as their growth is not as vigorous as seed-grown plants. This is because clones don’t grow taproots. Instead, they have secondary roots from their parent stem. In most cases, their growth is lateral, as opposed to downward. Taproots help plants to dig deep into the ground, reaching water that is not near the ground level. This is important for plants grown outdoors. However, for indoor growers, this is not important as taproots cannot develop in a container environment.
Growing cannabis from seeds
If you choose to grow your Cannabis from seeds, it’s always important to find the right high-quality seeds. Using standard seeds, you can expect between a quarter and one-third of the seeds to reach maturity.
When buying seeds, you want to make sure they are matured, dark brown colour with lighter accents, and a hard shell. You don’t want a seed that feels soft, fresh, and looks green, which points out that the seed hasn’t reached its maturity.
Always remember to use undamaged, grey, or dark brown seeds. They are more likely to germinate than whitish, cracked, or light tan seeds. Rosenthal writes, “Most guide books suggest that growers select the largest seeds in a batch for planting, but the size of the seed is genetically as well as environmentally determined and does not necessarily to its germination and seedling potential.”
Benefits of growing from seeds
- You have different options to buy any strain you want. Getting clones in different strains is sometimes impossible.
- If you buy high-quality seeds, you can get a better yield than from same-strain clones.
- You enjoy the growing process from the beginning.
Downsides of growing from seeds
- It’s time-consuming, as seeds need approximately 10 days in the germination stage and another couple of weeks to catch up clones at the beginning of the vegetative stage. In total, the germination and seedling stages take around 4-6 weeks.
- Unless you’re growing for breeding, you’ll have to identify the male plants and remove them before they reach pollination stage. This grueling task requires time and identification skills.
- You run the risk of a lower plant population after removing the male plants.
Cannabis germination & seedling
The seed contains all the genetic characteristics of the plant. It is the result of sexual reproduction, which takes the genes from both parents, male and female. Some plants are also intersexual or hermaphrodites. This occurs when one plant exhibits both male and female characteristics.
Genes in sequence determine the outcome of the plant in terms of size, disease and pest resistance, and root growth. It also determines foliage and flower growth and well as CBD or THC content. The genetic composition is a key factor in determining how well a plant will grow under artificial or natural light.
As noted earlier in this germination and seedling guide, mature brownish, dark-brown, or spotted seeds make the best planting materials. Avoid pale or green seeds because they are immature and will germinate poorly and increase their chance of disease and pest attack. Dry, mature seedlings of less than a year often germinate quickly and produce steady plants. You can acquire cannabis seeds from an array of sources and can vary in quality.
We always recommend buying the highest quality cannabis seeds (price varies from $40 to 400 per pack with 10-12 seeds) from reliable sources only. You can buy marijuana seeds at a dispensary (if your state is with adult-use legalization or a medical marijuana program), from seed banks (where you can find seeds from a variety of different breeders) and online (from the specific seed breeder’s website). Unfortunately, US federal law still prohibits cannabis, so it can be hard to find specific information on seed banks. Best ones are in the Netherlands or Spain, where the cannabis laws are less restricted. Therefore, the easiest way if you live in a state where marijuana is legal is to buy seeds from a dispensary or from breeders online. SoHum Seed Collective or Exotic Genetix is well-known breeders in the US, with a positive reputation you can trust. In Europe Sensi Seeds, Green House Seeds and Dinafem are good places to buy from.
Conditions for germination
Seeds need moisture, warmth, and oxygen to germinate. Soaking them in water allows moisture to seep through the protective seed coat in minutes. Moisture helps in activating “sleeping” hormones. Over the next 24-72 hours, the hormones become active and send a signal to the root.
Besides, humidity is essential and must be in a constant flow to transport fertilizers, hormones, and water to keep the plant growing and developing. Lack of moisture hinders the growth process. For best results, use distilled water. The optimum temperature for seed germination is 77°F (25 degrees Celsius). Temperatures below 21 degrees Celsius delay germination while those higher than 32 degrees Celsius lead to poor germination. You should avoid high temperatures and low levels of light, which can affect germination.
Oxygen is an important aspect of the process, without which the seed cannot germinate. If you push the seed too deep into the ground, it might not get adequate oxygen. Before germination, the seedlings do not have enough energy to penetrate much of the ground, so it’s advisable to plant shallow depths of less than 0.5 cm or twice the width of the seed.
When the seed begins to spread out the root, it experiences accelerated growth of the cells and the stem, resulting in rapid foliage and root development. The seedlings often go into the vegetative phase within 4-6 weeks, depending on the root development.
The practical process

Seed selection and soaking
Start by soaking the seeds in a container with distilled water for 24 hours (if seeds are older, a good practice is to soak in carbonated water enriched with fulvic acid, germination booster, hydrogen peroxide, or gibberellic acid). Do not soak longer because the seeds may begin to rot. Initially, the seeds will float to the surface but when water penetrates, they sink to the bottom of the container. Seeds that fail to sink after 24 hours are unlikely to survive.
Draining the water
Use a pan or grill that will allow water to drain. Put a paper towel over it and moisten it with distilled water so it’s well saturated and moist. Drain the water out of the pan and place the seeds on a damp paper towel. Alternatively, you can use a cosmetic cotton disk instead of paper towel.
Apply a few more damp layers. Allow excess water to settle and place the pan with seeds in low light, humid place about 75-80°F (24-27° degrees Celsius). This is ideal for a fridge top. Check daily, and don’t let the towels dry up or soak on more water, as the seeds will need moisture and oxygen. The idea is to let the towels remain moist to provide the moisture needed by the seeds. Check after a few days to see whether the root begins to appear.
Planting the seeds
Once the seeds have broken down and the white root appears, the seeds are ready for planting. This should happen within three days. Seeds that have not grown roots within this period are unlikely to germinate. Prepare your sprouting cubes by draining them with water until they are saturated and well-drained.
Cannabis seedlings do not have enough energy to penetrate the ground, so don’t place them so deep inside. With the help of a pen, make small holes in the ground, about twice the size of the seed. Using tweezers, insert the seed into the hole, root down. If you use soil instead of sprouting cubes, cover the top with soil and lightly press to prevent the seed from direct exposure to sunlight. Good practice to use seed propagator and put it under fluorescent (CFL) or LED light for 24 hours a day. Many growers, until the flowering stage, use 18 hours of light, but practically in many cases is easier to control the environment using 24 hours of light.
From now on until the flowering stage, the best environment is 70-75% humidity and 77-80°F (25-27° degrees Celsius) temperature. The best practice is to use LED or CFL lights in this stage. Not recommended to use HPS as it produces a lot of heat and too much light.
Seedlings appear
After about 4-6 days, the cannabis seedling should penetrate the ground and the first embryonic leaves should be visible. After 7-10 days, the first true leaves of the plant should appear.
The embryonic leaves, which are the first to appear, are smooth and have no “teeth” around their edges. The most common “true” leaves are classic cannabis leaves with “teeth” around and a pointed tip. After 10-14 days, the “true” leaves should be more significant or at least similar in size to the embryonic leaves. Some growers give fertilizer at this cannabis seedling stage, but it’s absolutely not necessary. The most important thing to do at this stage is to keep the soil moist so the plants can develop foliage, get oxygen, and grow roots quickly.
Transplanting
After 2-3 weeks, the plants should have two or three pairs of true leaves. At this stage, they’re ready for transplanting to a higher-capacity pot. Most growers use one-liter pots for transplanting where the plant grows and receives food according to the instructions given by the fertilizer company at this stage. It’s the end of the cannabis seedling stage and the beginning of the vegetative phase where the plant starts to grow fast. This is a critical period for the plants so it requires a lot of attention.
If you were using sprouting cubes, when transplanting to one-liter pots, put the whole cube to the soil. But not too deep, just to be able to cover the top with the soil.
Be careful not to let the ground dry. If you’re growing from clones, you get the plants in this stage where you need to transplant them to one-liter pots. We recommend using Light Mix – a lightly fertilized organic soil mixed with perlite.
Soil is key, absolutely key. If there is one aspect of growing marijuana that you shouldn’t screw up then it’s the soil. Don’t just use dirt from the backyard or any old soil from the hardware store. Marijuana soil should contain all the essential nutrients and properties that the plant needs to grow. Picking good soil can also save you money because you’re picking dirt that has already been infused with nutrients. – Ed Rosenthal ‘Marijuana Grower’s Hanbook’
As mentioned before, keep the air temperature around 80°F (27° Celsius) and humidity at 70-75 percent.
Lighting
Light is a definite requirement for growing any living plant, and marijuana is no different. After transplanting to one-liter pots, you can start using your LEDs or HPS lights. If you’re using the HPS lighting, just ensure it’s on the lowest power (250W). Keep the light as much high from the plant as possible. After one week, you can adjust the lighting power to 450W.
From this point, if you’re not using auto-flower strain, you can grow your plants giving them 24 or 18 hours of light as much as you want, until the flowering stage, when you decide to put them under 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness. In the vegetative stage, you should form the plant branches (lollipoping, pruning, and etc). We’ll cover more of this in our next guide.
Problems associated with cannabis seedlings
The main problems faced by newbie growers at these stages are too much or too little watering. Try to keep the soil evenly moist but not too wet, and don’t let it dry up. To test the level of moisture, put a finger inside the soil about 10-15 mm. If the finger comes out dry, the soil needs watering. Usually, apply water at least twice a week for the first two weeks. Remember, the seedling has only a few roots to absorb water, and they’re very sensitive. The cannabis seedling process should take around four or six weeks when the plants start the vegetative phase.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the main types of cannabis plants?
There are three main types: Cannabis Sativa, Cannabis Indica, and Cannabis Ruderalis. Most of the strains on the commercial market today are hybrids between these types.
What Cannabis Ruderalis is used for?
Traditionally it is used in Russian and Mongolian folk medicine, especially for uses in treating depression. Moreover, because Ruderalis is auto-flowering subspecies, it’s perfect for breeding for the new auto-flowering strains.
What are the main stages of cannabis growth?
From seeds to harvest, the life cycle of cannabis growth can be divided into four main stages: Germination (5-10 days), Cannabis Seedling (2-4 weeks), Cannabis Vegetation (3-15 weeks), and Cannabis Flowering (8-11 weeks).
What are cannabis clones?
A cannabis clone is a cutting from a plant in the vegetative stage. It is genetically identical to the mother plant it was taken from. It means, if it was cut off from the female marijuana plant, you can be 100% sure the clone will be female too.
How to choose good quality cannabis seeds that are ready for the germination process?
When buying seeds, you want to make sure they are matured, dark brown color with lighter accents, and a hard shell. You don’t want a seed that feels soft, fresh, and looks green, which points out that the seed hasn’t reached its maturity.
What are the essential conditions needed for cannabis germination?
Seeds need moisture, warmth (77°F/25°C), and oxygen to germinate.
What are recommended pH solution levels during the germination and seedling stage (growing in soil)?
Your prepared food for the plants should have slightly acidic 5.8-6.0 pH levels. In the vegetation stage, increase it to 6.0 and during flowering 6.3 – 6.5. A Bluelab combo meter is a perfect tool for it. You can measure not only pH levels but conductivity and temperature too. The pH levels are always measured after you mix all the nutrients.


